Supercharge your API workflow
Modern software is built on APIs. Postman helps you develop APIs faster.
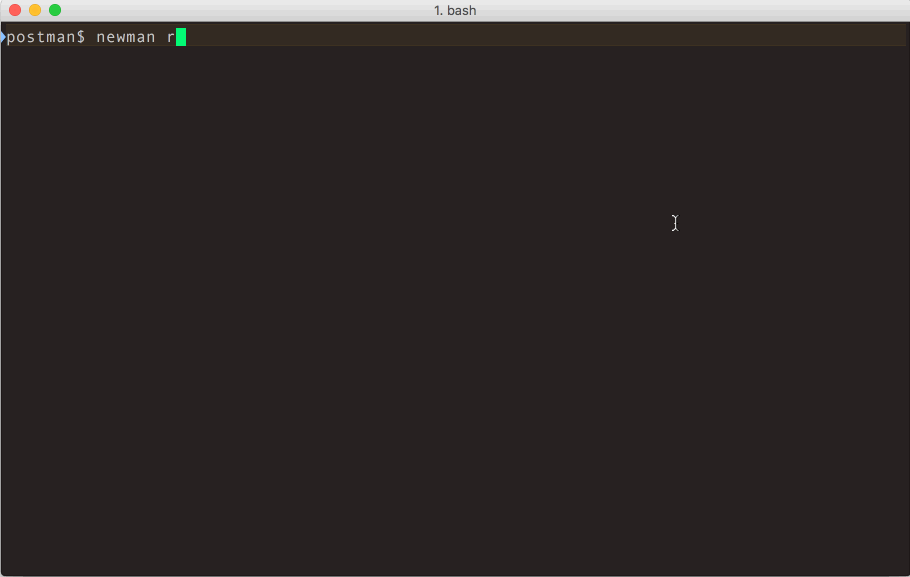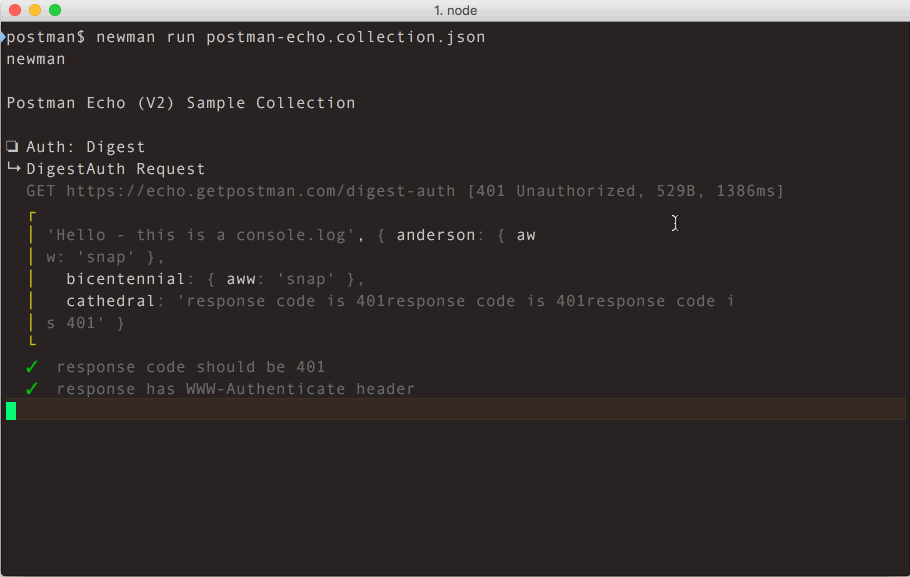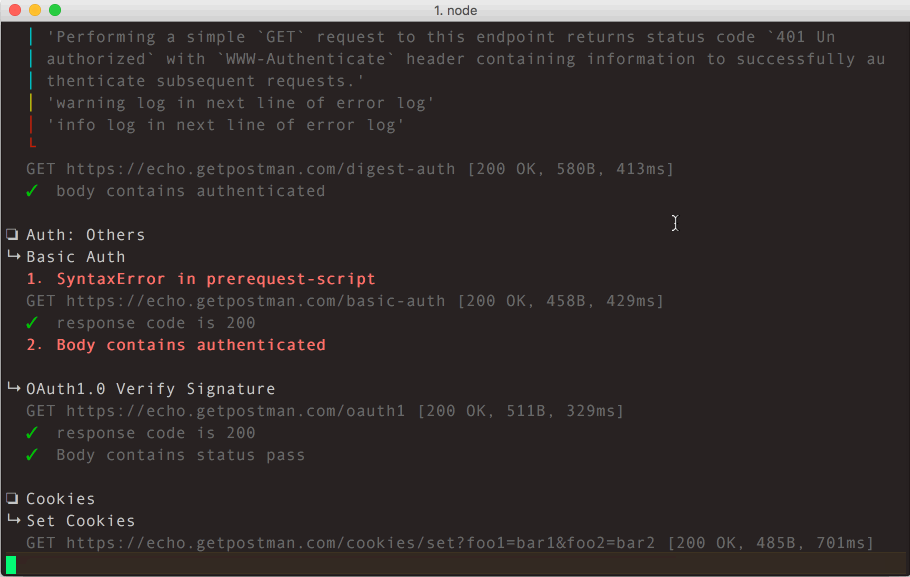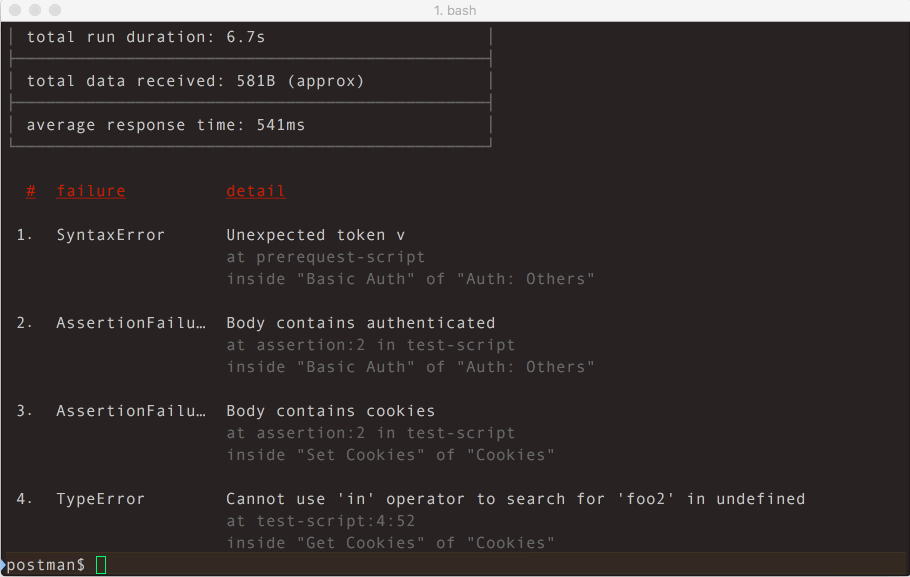
Using Newman, one can effortlessly run and test a Postman Collections directly from the command-line. It is built with extensibility in mind so that you can easily integrate it into your continuous integration servers and build systems.
For details on changes across v2 to v3, see the Newman v2 to v3 Migration Guide
For Newman v2.x release documentation, see the Newman v2.x README.
To run Newman, ensure that you have NodeJS >= v4. A copy of the NodeJS installable can be downloaded from https://nodejs.org/en/download/package-manager.
The easiest way to install Newman is using NPM. If you have NodeJS installed, it is most likely that you have NPM installed as well.
$ npm install newman --global;
The newman run command allows you to specify a collection to be run. You can easily export your Postman
Collection as a json file from the Postman App and run it using Newman.
$ newman run examples/sample-collection.json;
If your collection file is available as an URL (such as from our Cloud API service), Newman can fetch your file and run it as well.
$ newman run https://www.getpostman.com/collections/631643-f695cab7-6878-eb55-7943-ad88e1ccfd65-JsLv;
For the complete list of options, refer the Commandline Options section below.
Newman can be easily used within your JavaScript projects as a NodeJS module. The entire set of Newman CLI functionality is available for programmatic use as well. The following example runs a collection by reading a JSON collection file stored on disk.
var newman = require('newman'); // require newman in your project
// call newman.run to pass `options` object and wait for callback
newman.run({
collection: require('./sample-collection.json'),
reporters: 'cli'
}, function (err) {
if (err) { throw err; }
console.log('collection run complete!');
});Note: The newman v2.x .execute function has been discontinued.
-
-e <source>,--environment <source>
Specify an environment file path or URL. Environments provide a set of variables that one can use within collections. Read More -
-g <source>,--globals <source>
Specify file path or URL for global variables. Global variables are similar to environment variables but has a lower precedence and can be overridden by environment variables having same name. -
-d <source>,--iteration-data <source>
Specify a data source file (CSV) to be used for iteration as a path to a file or as a URL. Read More -
-n <number>,--iteration-count <number>
Specifies the number of times the collection has to be run when used in conjunction with iteration data file. -
--folder <name>
Run requests within a particular folder in a collection. -
--export-environment <path>
The path to the file where Newman will output the final environment variables file before completing a run. -
--export-globals <path>
The path to the file where Newman will output the final global variables file before completing a run. -
--export-collection <path>
The path to the file where Newman will output the final collection file before completing a run. -
--timeout-request <ms>
Specify the time (in milliseconds) to wait for requests to return a response. -
-k,--insecure
Disables SSL verification checks and allows self-signed SSL certificates. -
--ignore-redirects
Prevents newman from automatically following 3XX redirect responses. -
--delay-request
Specify the extent of delay between requests (milliseconds). -
--bail
Specify whether or not to stop a collection run on encountering the first error. -
-x,--suppress-exit-code
Specify whether or not to override the default exit code for the current run. -
--color
Use this option to force colored CLI output (for use in CLI for CI / non TTY environments). -
--no-color
Newman attempts to automatically turn off color output to terminals when it detects the lack of color support. With this property, one can forcibly turn off the usage of color in terminal output for reporters and other parts of Newman that output to console. -
--disable-unicode
Specify whether or not to force the unicode disable option. When supplied, all symbols in the output will be replaced by their plain text equivalents. -
--global-var "<global-variable-name>=<global-variable-value>"
Allows the specification of global variables via the command line, in a key=value format. Multiple CLI global variables can be added by using--global-varmultiple times, like so:--global-var "foo=bar" --global-var "alpha=beta".
Reporters provide information about the current collection run in a format that is easy to both: disseminate and assimilate.
-
-r <reporter-name>,--reporters <reporter-name>
Specify one reporter name asstringor provide more than one reporter name as a comma separated list of reporter names. Available reporters are:cli,json,htmlandjunit.
Spaces should not be used between reporter names / commas whilst specifying a comma separted list of reporters. For instance:
✅-r html,cli,json,junit
❌-r html, cli , json,junit -
--reporter-{{reporter-name}}-{{reporter-option}}
When multiple reporters are provided, if one needs to specifically override or provide an option to one reporter, this is achieved by prefixing the option with--reporter-{{reporter-name}}-.
For example,... --reporters cli,html --reporter-cli-silentwould silence the CLI reporter only. -
--reporter-{{reporter-options}}
If more than one reporter accepts the same option name, they can be provided using the common reporter option syntax. <br /
For example,... --reporters cli,html --reporter-silentpasses thesilent: trueoption to both HTML and CLI reporter.
Note: Sample collection reports have been provided in examples/reports.
These options are supported by the CLI reporter, use them with appropriate argument switch prefix. For example, the
option no-summary can be passed as --reporter-no-summary or --reporter-cli-no-summary.
CLI reporter is enabled by default, you do not need to specifically provide the same as part of --reporters option.
However, enabling one or more of the other reporters will result in no CLI output. Explicitly enable the CLI option in
such a scenario.
| CLI Option | Description |
|---|---|
--reporter-cli-silent |
The CLI reporter is internally disabled and you see no output to terminal. |
--reporter-cli-no-summary |
The statistical summary table is not shown. |
--reporter-cli-no-failures |
This prevents the run failures from being separately printed. |
--reporter-cli-no-assertions |
This turns off the request-wise output as they happen. |
--reporter-cli-no-console |
This turns off the output of console.log (and other console calls) from collection's scripts. |
The built-in JSON reporter is useful in producing a comprehensive output of the run summary. It takes the path to the
file where to write the file. The content of this file is exactly same as the summary parameter sent to the callback
when Newman is used as a library.
To enable JSON reporter, provide --reporters json as a CLI option.
| CLI Option | Description |
|---|---|
--reporter-json-export <path> |
Specify a path where the output JSON file will be written to disk. If not specified, the file will be written to newman/ in the current working directory. |
The built-in HTML reporter produces and HTML output file outlining the summary and report of the Newman run. To enable the
HTML reporter, provide --reporters html as a CLI option.
| CLI Option | Description |
|---|---|
--reporter-html-export <path> |
Specify a path where the output HTML file will be written to disk. If not specified, the file will be written to newman/ in the current working directory. |
--reporter-html-template <path> |
Specify a path to the custom template which will be used to render the HTML report. This option depends on --reporter html and --reporter-html-export being present in the run command. If this option is not specified, the default template is used |
Custom templates (currently handlebars only) can be passed to the HTML reporter via --reporter-html-template <path> with --reporters html and --reporter-html-export.
The default template is used in all other cases.
Newman can output a summary of the collection run to a JUnit compatible XML file. To enable the JUNIT reporter, provide
--reporters junit as a CLI option.
| CLI Option | Description |
|---|---|
--reporter-junit-export <path> |
Specify a path where the output XML file will be written to disk. If not specified, the file will be written to newman/ in the current working directory. |
Older command line options are supported, but are deprecated in favour of the newer v3 options and will soon be discontinued. For documentation on the older command options, refer to README.md for Newman v2.X.
Newman also supports custom reporters, provided that the reporter works with Newman's event sequence. Working examples on how Newman reporters work can be found in lib/reporters. For instance, to use the Newman teamcity reporter:
- Install the reporter package. Note that the name of the package is of the form
newman-reporter-<name>. The installation should be global if newman is installed globally, local otherwise. (Replace-gfrom the command below with-Sfor a local installation.
npm install -g newman-reporter-teamcity
- Use the installed reporter, either via the CLI, or programmatic usage. Here, the
newman-reporterprefix is not required while specifying the reporter name in the options.
newman run /path/to/collection.json -r cli,teamcity
var newman = require('newman');
newman.run({
collection: '/path/to/collection.json',
reporters: ['cli', 'teamcity']
}, process.exit);Client certificates are an alternative to traditional authentication mechanisms. These allow their users to make authenticated requests to a server, using a public certificate, and an optional private key that verifies certificate ownership. In some cases, the private key may also be protected by a secret passphrase, providing an additional layer of authentication security.
Newman supports SSL client certificates, via the following CLI options (available with Newman v3 style run only):
-
--ssl-client-cert
The path to the public client certificate file. -
--ssl-client-key
The path to the private client key (optional). -
--ssl-client-passphrase
The secret passphrase used to protect the private client key (optional).
-
-h,--help
Show commandline help, including a list of options, and sample use cases. -
-v,--version
Displays the current Newman version, taken from package.json
Newman can also be configured to work with proxy settings via the following environment variables:
HTTP_PROXY/http_proxyHTTPS_PROXY/https_proxyNO_PROXY/no_proxy
For more details on using these variables, please see https://github.com/postmanlabs/postman-request/blob/master/README.md#controlling-proxy-behaviour-using-environment-variables
The run function executes a collection and returns the run result to a callback function provided as parameter. The
return of the newman.run function is a run instance, which emits run events that can be listened to.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| options | This is a required argument and it contains all information pertaining to running a collection. Required Type: object |
| options.collection | The collection is a required property of the options argument. It accepts an object representation of a Postman Collection which should resemble the schema mentioned at https://schema.getpostman.com/. The value of this property could also be an instance of Collection Object from the Postman Collection SDK.As string, one can provide a URL where the Collection JSON can be found (e.g. Postman Cloud API service) or path to a local JSON file.Required Type: `object |
| options.environment | One can optionally pass an environment file path or URL as string to this property and that will be used to read Postman Environment Variables from. This property also accepts environment variables as an object. Environment files exported from Postman App can be directly used here.Optional Type: `object |
| options.globals | Postman Global Variables can be optionally passed on to a collection run in form of path to a file or URL. It also accepts variables as an object.Optional Type: `object |
| options.iterationCount | Specify the number of iterations to run on the collection. This is usually accompanied by providing a data file reference as options.iterationData.Optional Type: number, Default value: 1 |
| options.iterationData | Path to the JSON or CSV file or URL to be used as data source when running multiple iterations on a collection. Optional Type: string |
| options.folder | The name or ID of the folder (ItemGroup) in the collection which would be run instead of the entire collection. Optional Type: string |
| options.timeoutRequest | Specify the time (in milliseconds) to wait for requests to return a response. Optional Type: number, Default value: Infinity |
| options.delayRequest | Specify the time (in milliseconds) to wait for between subsequent requests. Optional Type: number, Default value: 0 |
| options.ignoreRedirects | This specifies whether newman would automatically follow 3xx responses from servers. Optional Type: boolean, Default value: false |
| options.insecure | Disables SSL verification checks and allows self-signed SSL certificates. Optional Type: boolean, Default value: false |
| options.bail | A boolean switch to specify whether or not to gracefully stop a collection run on encountering the first error. Takes no arguments. Optional Type: boolean, Default value: false |
| options.suppressExitCode | If present, allows overriding the default exit code from the current collection run, useful for bypassing collection result failures. Takes no arguments. Optional Type: boolean, Default value: false |
| options.reporters | Specify one reporter name as string or provide more than one reporter name as an array.Available reporters: cli, json, html and junit.Optional Type: `string |
| options.reporter | Specify options for the reporter(s) declared in options.reporters. e.g. reporter : { junit : { export : './xmlResults.xml' } } e.g. reporter : { html : { export : './htmlResults.html', template: './customTemplate.hbs' } } Optional Type: object |
| options.color | Forces colored CLI output (for use in CI / non TTY environments). Optional Type: boolean |
| options.noColor | Newman attempts to automatically turn off color output to terminals when it detects the lack of color support. With this property, one can forcibly turn off the usage of color in terminal output for reporters and other parts of Newman that output to console. Optional Type: boolean |
| options.sslClientCert | The path to the public client certificate file. Optional Type: string |
| options.sslClientKey | The path to the private client key file. Optional Type: string |
| options.sslClientPassphrase | The secret client key passphrase. Optional Type: string |
| callback | Upon completion of the run, this callback is executed with the error, summary argument.Required Type: function |
The callback parameter of the newman.run function receives two arguments: (1) error and (2) summary
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| error | In case newman faces an error during the run, the error is passed on to this argument of callback. By default, only fatal errors, such as the ones caused by any fault inside Newman is passed on to this argument. However, setting abortOnError:true or abortOnFailure:true as part of run options will cause newman to treat collection script syntax errors and test failures as fatal errors and be passed down here while stopping the run abruptly at that point.Type: object |
| summary | The run summary will contain information pertaining to the run. Type: object |
| summary.error | An error object which if exists, contains an error message describing the message Type: object |
| summary.collection | This object contains information about the collection being run, it's requests, and their associated pre-request scripts and tests. Type: object |
| summary.environment | An object with environment variables used for the current run, and the usage status for each of those variables. Type: object |
| summary.globals | This object holds details about the globals used within the collection run namespace. Type: object |
| summary.run | A cumulative run summary object that provides information on . Type: object |
| summary.run.stats | An object which provides details about the total, failed, and pending counts for pre request scripts, tests, assertions, requests, and more. Type: object |
| summary.run.failures | An array of failure objects, with each element holding details, including the assertion that failed, and the request. Type: array.<object> |
| summary.run.executions | This object contains information about each request, along with it's associated activities within the scope of the current collection run. Type: array.<object> |
Newman triggers a whole bunch of events during the run.
newman.run({
collection: require('./sample-collection.json'),
data: [{ "var": "data", "var_beta": "other_val" }],
globals: {
"id": "5bfde907-2a1e-8c5a-2246-4aff74b74236",
"name": "test-env",
"values": [
{
"key": "alpha",
"value": "beta",
"type": "text",
"enabled": true
}
],
"timestamp": 1404119927461,
"_postman_variable_scope": "globals",
"_postman_exported_at": "2016-10-17T14:31:26.200Z",
"_postman_exported_using": "Postman/4.8.0"
},
environment: {
"id": "4454509f-00c3-fd32-d56c-ac1537f31415",
"name": "test-env",
"values": [
{
"key": "foo",
"value": "bar",
"type": "text",
"enabled": true
}
],
"timestamp": 1404119927461,
"_postman_variable_scope": "environment",
"_postman_exported_at": "2016-10-17T14:26:34.940Z",
"_postman_exported_using": "Postman/4.8.0"
}
}).on('start', function (err, args) { // on start of run, log to console
console.log('running a collection...');
}).on('done', function (err, summary) {
if (err || summary.error) {
console.error('collection run encountered an error.');
}
else {
console.log('collection run completed.');
}
});All events receive two arguments (1) error and (2) args. The list below describes the properties of the second
argument object.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| start | The start of a collection run |
| beforeIteration | Before an iteration commences |
| beforeItem | Before an item execution begins (the set of prerequest->request->test) |
| beforePrerequest | Before prerequest script is execution starts |
| prerequest | After prerequest script execution completes |
| beforeRequest | Before an HTTP request is sent |
| request | After response of the request is received |
| beforeTest | Before test script is execution starts |
| test | After test script execution completes |
| beforeScript | Before any script (of type test or prerequest) is executed |
| script | After any script (of type test or prerequest) is executed |
| item | When an item (the whole set of prerequest->request->test) completes |
| iteration | After an iteration completes |
| assertion | This event is triggered for every test assertion done within test scripts |
| console | Every time a console function is called from within any script, this event is propagated |
| exception | When any asynchronous error happen in scripts this event is triggered |
| beforeDone | An event that is triggered prior to the completion of the run |
| done | This event is emitted when a collection run has completed, with or without errors |
Newman also supports file uploads for request form data. The files must be present in the current working directory. Your collection must also contain the filename in the "src" attribute of the request.
In this collection, sample-file.txt should be present in the current working directory.
{
"info": {
"name": "file-upload"
},
"item": [
{
"request": {
"url": "https://postman-echo.com/post",
"method": "POST",
"body": {
"mode": "formdata",
"formdata": [
{
"key": "file",
"type": "file",
"enabled": true,
"src": "sample-file.txt"
}
]
}
}
}
]
}$ ls
file-upload.postman_collection.json sample-file.txt
$ newman run file-upload.postman_collection.json
1 Generate an API key
2 Fetch a list of your collections from: https://api.getpostman.com/collections?apikey=$apiKey
3 Get the collection link via it's uid: https://api.getpostman.com/collections/$uid?apikey=$apiKey
4 Obtain the environment URI from: https://api.getpostman.com/environments?apikey=$apiKey
5 Using the collection and environment URIs acquired in steps 3 and 4, run the collection as follows:
newman run https://api.getpostman.com/collections/$uid?apikey=$apiKey \
--environment https://api.getpostman.com/environments/$uid?apikey=$apiKey
If you are interested in talking to the team and other Newman users, we are there on Slack. Feel free to drop by and say hello. Our upcoming features and beta releases are discussed here along with world peace.
Get your invitation for Postman Slack Community from: https://www.getpostman.com/slack-invite.
Already member? Sign in at https://postmancommunity.slack.com
This software is licensed under Apache-2.0. Copyright Postdot Technologies, Inc. See the LICENSE.md file for more information.