This is a lightweight 2D simulator of the MIT Racecar. It can be built with ROS, or it can be used as a standalone C++ library.
If you have ros-melodic-desktop installed, the additional dependencies you must install are:
- tf2_geometry_msgs
- ackermann_msgs
- joy
- map_server
You can install them by running:
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-tf2-geometry-msgs ros-melodic-ackermann-msgs ros-melodic-joy ros-melodic-map-server
The full list of dependencies can be found in the package.xml file.
To install the simulator package, clone it into your catkin workspace:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/mit-racecar/racecar_simulator.git
Then run catkin_make to build it:
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
To run the simulator on its own, run:
roslaunch racecar_simulator simulate.launch
This will launch everything you need for a full simulation; roscore, the simulator, a preselected map, a model of the racecar and the joystick server.
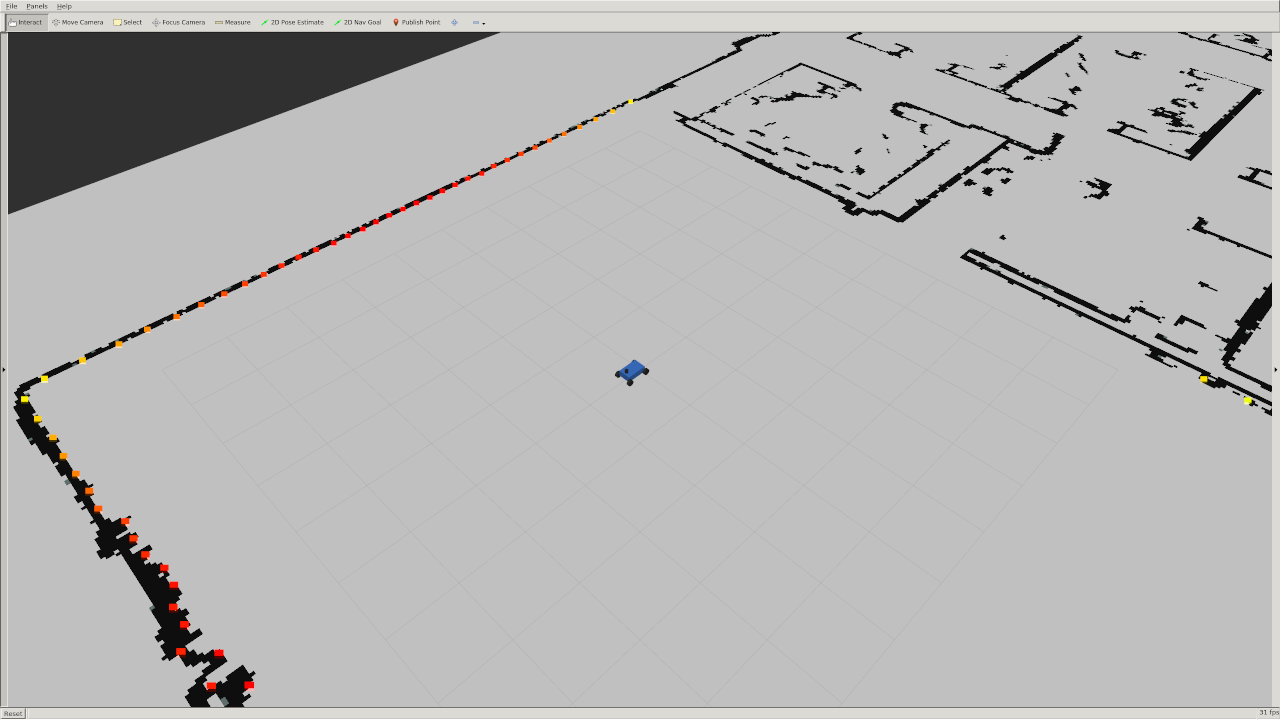
With the simulator running, open rviz.
In the left panel at the bottom click the "Add" button, then in the "By topic" tab add the /map topic and the /scan topic.
Then in the "By display type" tab add the RobotModel type.
In the left panel under the newly added LaserScan section, change the size to 0.1 meters for a clearer visualization of the lidar (shown in rainbow).
You should see the car sitting in the middle of a 2D map of MIT's building 31 as shown below:
You can use a USB joystick to drive the car around, or you can place the car manually by clicking the "2D Pose Estimate button" on the top of the screen and dragging your mouse on the desired pose.
To make the car drive autonomously, publish AckermannDrive messages to the /drive topic.
To instantly move the car to a new state publish Pose messages to the /pose topic. This can be useful for scripting the car through a series of automated tests.
The simulated lidar is published to the /scan topic as LaserScan messages.
The pose of the car is broadcast as a transformation between the map frame and the base_link frame. base_link is the center of the rear axis. The laser frame defines the frame from which the lidar scan is taken and another transform is broadcast between it and base_link.
The parameters listed below can be modified in the params.yaml file.
drive_topic: The topic to listen to for autonomous driving.
joy_topic: The topic to listen to for joystick commands.
map_topic: The topic to listen to for maps to use for the simulated scan.
pose_topic: The topic to listen to for instantly setting the position of the car.
pose_rviz_topic: The topic to listen to for instantly setting the position of the car with Rviz's "2D Pose Estimate" tool.
scan_topic: The topic to publish the simulated scan to.
distance_transform_topic: The topic to publish a distance transform to for visualization (see the implimentation section below).
base_link: The frame of the car, specifically the center of the rear axle.
scan_frame: The frame of the lidar.
map_frame: The frame of the map.
update_pose_rate: The rate at which the simulator will publish the pose of the car and simulated scan, measured in seconds. Since the dynamics of the system are evaluated analytically, this won't effect the dynamics of the system, however it will effect how often the pose of the car reflects a change in the control input.
wheelbase: The distance between the front and rear axle of the racecar, measured in meters. As this distance grows the minimum turning radius of the car increases.
max_speed: The maximum speed of the car in meters per second.
max_steering_angle: The maximum steering angle of the car in radians.
scan_beams: The number of beams in the scan.
scan_field_of_view: The field of view of the lidar, measured in radians. The beams are distributed uniformly throughout this field of view with the first beam being at -scan_field_of_view and the last beam being at scan_field_of_view. The center of the field of view is direction the racecar is facing.
scan_distance_to_base_link: The distance from the lidar to the center of the rear axle (base_link), measured in meters.
scan_std_dev: The ammount of noise applied to the lidar measuredments. The noise is gaussian and centered around the correct measurement with standard deviation scan_std_dev, measured in meters.
map_free_threshold: The probability threshold for points in the map to be considered "free". This parameter is used to determine what points the simulated scan hits and what points it passes through.
joy: This boolean parameter enables the joystick if true.
joy_speed_axis: The index of the joystick axis used to control the speed of the car. To determine this parameter it may be useful to print out the joystick messages with rostopic echo /joy.
joy_angle_axis: The index of the joystick axis used to control the angle of the car. To determine this parameter it may be useful to print out the joystick messages with rostopic echo /joy.
joy_max_speed: The maximum speed the joystick is able to propel the car, measured in meters per second.
Distance transform. Ackermann kinematics
- Finish documentation
- Simulate odometry and imu
- Add colision detection?