In my 15 years of designing and developing more than 100 java web applications, I have learnt that techies love coining new terminologies. They are great as we don't need to explain each time but imagine the state of a beginning programmer or a non techie - a Tester or Business Analyst or your Product Owner. They hardly understand them. This guide is to demystify these terms through videos!
As I find time, I will create more videos. Request some patience :)
If you think, I'm missing an important topic, shoot an email or create a pull request!
If you have a great video for one of these topics, which does not have a video attached, submit a pull request!
- 1: FOLLOW Ranga on LinkedIn
- 1: AWS Roadmap
- 2: Azure Roadmap
- 3: Google Cloud Roadmap
- 4: Cloud Beginner Roadmap
- 5: DevOps Roadmap
- 6: Java Full Stack Roadmap
- 7: Java Microservices Roadmap
- Java
- Spring
- Spring Boot
- Spring MVC
- Spring Data
- Spring Data Flow
- Spring Data Rest
- Spring Cloud
- Spring Batch
- Spring Initializr
- Spring Security
- Spring HATEOAS
- Spring Integration
- Unit Testing
- JUnit
- Mockito
- EasyMock
- PowerMock
- Cobertura
- Emma
- Database
- Hibernate
- iBatis
- Rest Services
- Jersey Framework
- Play Framework
- Spring REST (actually Spring MVC)
- Others
- Quartz
- Guava
- Guice
- EhCache
- Drools
- Apache Commons
- JavaScript
- NodeJS
- JQuery
- AngularJS
- Ember.js
- React.js
- Redux
- ECMAScript
- CSS
- Bootstrap
- Formats
- XML
- XPath
- JSON
- SOAP
- Swagger
- Spring Rest Docs
- Others
- jHipster
- JDK
- JVM
- JRE
- JAR
- WAR
- EAR
- Classloader
- Annotations
- Platform Independence
- OOPS
- Interface
- Inheritance
- Abstract Class
- Coupling
- Cohesion
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Mocking and Mock objects
- Dependency Management
- Readable Code
- Dependency Injection
- Inversion of Control
- Synchronization
- Logging
- Caching
- Exception Handling
- Cross Cutting Concerns
- Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP)
- Spring
- Autowiring
- Component Scan
- Application Context
- Coding Standards
- Code Review
- Refactoring
- Pair Programming
- Unit Testing
- Automation Testing
- Load Testing
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
- Test Driven Development (TDD)
- Behavior Driven Development (BDD)
- Acceptance Test Driven Development (ATDD)
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Continuous Delivery (CD)
- DevOps
- Cloud
- Big Data
- Microservices
- Cloud Native Applications
- 12 factor app
- Micro front-end
- HATEOAS
- Functional Programming
- Reactive Programming
- In memory Database
- SPA (Single Page Application)
- Code Quality
- Technical Debt
- Code Coverage
- Legacy Code
- Tech Design
- Evolutionary Design
- Code First
- Contract First
- Web Service
- RESTful Web Service
- Static Code Analysis (Security)
- Vertical Slice
- Internationalization or Localization
- Transaction Management
- NFR (Non Functional Requirements)
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Performance
- Scalability
- Load Balancing
- Availability
- Resilience
- Maintainability
- Portability
- Security
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- SQL Injection
- Containerization
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javaee/tech/index.html
- Batch Applications for the Java Platform - JSR 352
- Contexts and Dependency Injection for Java 1.1 - JSR 346
- Dependency Injection for Java 1.0 - JSR 330
- Java Persistence 2.1 - JSR 338
- Java Message Service API 2.0 - JSR 343
- Java Transaction API (JTA) 1.2 - JSR 907
- Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS) 2.0 - JSR 339
- Java API for XML-Based Web Services (JAX-WS) 2.2 - JSR 224
- Java Authentication Service Provider Interface for Containers 1.1 - JSR 196
- Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB) - JSR 222
- Java Database Connectivity 4.0 - JSR 221
- Java Management Extensions (JMX) 2.0 - JSR 003
- JSTL
- Design Patterns
- 4 Principles of Simple Design
- SOLID principles
- UML
- IDE
- Eclipse
- NetBeans
- Intellij
- Code Quality
- SonarQube
- CheckStyle
- PMD
- Findbugs
- Application/Web/Http Servers
- Tomcat
- WebSphere
- Weblogic
- Lightweight
- Jetty
- Undertow
- API Gateways
- Distributed Cache
- Hazelcast
- Databases
- In memory
- H2
- HSQL
- Big Data
- Mongo DB
- Redis
- Build
- Ant
- Maven
- Gradle
- Nexus
- Message Brokers
- Kafka
- Performance
- jProfiler
- VisualVM
- Productivity
- jRebel
- Continuous Integration
- Jenkins
- Automation Testing
- Selenium
- Integration
- Camel
- Spring Integration
- ESB
- BDD
- Cucumber
- Version Control
- Git
- Stash
- SVN
- Containerization
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- DevOps
- Chef
- CMS
- Load Testing
- JMeter
- Agile
- Scrum
- Kanban
- Waterfall
The Spring Framework is a Java platform that provides comprehensive infrastructure support for developing Java applications. Spring handles the infrastructure so you can focus on your application. http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/html/overview.html
COMING SOON..
- Lets Programmers focus on Business Logic
- Key feature is Dependency Management
- Enables Testability
- Inversion of Control
- Application Context
- Why is Unit Testing Important?
- Loose Coupling
- Testable Code
- Plumbing Code
- JDBC
- JMS
- Clean Architecture
- Easy implementation of cross cutting concerns
- Architectural Flexibility
- Integration with other frameworks
- Design Patterns
- Add a Maven Dependency
- Use Spring Initializr
- Consider Spring Boot
- Write Unit Tests
- Use BOM
- Use Maven or Gradle
- Difficult for Starting Programmer to understand
- Once You understand, you cannot stop using it!
- Spring Modules https://github.com/in28minutes/SpringIn28Minutes/blob/master/Spring%20Tutorial%20For%20Beginners%20with%20Examples_v2.pdf
- Spring Projects http://spring.io/projects
- Spring Initializr https://start.spring.io
https://www.udemy.com/course/spring-tutorial-for-beginners/
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run". We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration. http://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/
COMING SOON.. Fingers crossed
- Reduces effort in starting up a project
- How long does it take to start a new project?
- What do you do in Sprint 0?
- Integrating Frameworks may be complex!
- Configuration Management
- Logging
- Transaction Management
- Error/ Exception Handling
- Monitoring & Health Checks
- Integrate Unit Testing and Mocking Frameworks
- Migrating to different version is tough
- Incompatible Jars - Jar Hell
- Which version of other frameworks (Hibernate etc..) to upgrade to?
- Reduce start up time of a project
- Microservice Architecture!
- No of small projects increase exponentially
- Starter Projects make integration with other frameworks easy
- spring-boot-starter-web-services - Starter for using Spring Web Services
- spring-boot-starter-web - Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container
- spring-boot-starter-test - Starter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including JUnit, Hamcrest and Mockito
- spring-boot-starter-hateoas - Starter for building hypermedia-based RESTful web application with Spring MVC and Spring HATEOAS
- spring-boot-starter-jersey - Starter for building RESTful web applications using JAX-RS and Jersey. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-web
- spring-boot-starter-security - Starter for using Spring Security
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa - Starter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
- spring-boot-starter-data-rest - Starter for exposing Spring Data repositories over REST using Spring Data REST
- Developer Tools
- Easy to debug and hot deploy!
- Spring Initializr https://start.spring.io
- You need to understand Spring to solve problems
- Standardize a little before you use Spring Boot in all your microservices
- Make sure to put right security around Actuator
- Can be deployed to Cloud Services easily.
ADD_LATER
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BjNhGaZDr0Y
- Great MVC & Rest Services Framework
- Loosely Coupled Design
- Support for multiple view technologies
- Integrates well with all popular frameworks
ADD_LATER
Spring Data REST is part of the umbrella Spring Data project and makes it easy to build hypermedia-driven REST web services on top of Spring Data repositories. http://projects.spring.io/spring-data-rest/ org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-rest
COMING SOON
- Expose Services from your Data without a lot of code
- Supports SQL based and No SQL based databases
- Pagination
- Filtering
- Sorting
- HATEOAS
- defaultPageSize
- Simple Projects want to quickly expose Rest Services
- Simplest way is to use the Spring Boot Starter Project
- Not recommended for Complex Applications
\pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.in28minutes</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-rest-example</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.7</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-release</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-release</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>
\src\main\java\com\in28minutes\Application.java
package com.in28minutes;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
\src\main\java\com\in28minutes\data\Todo.java
package com.in28minutes.data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Todo {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private long id;
private String user;
private String desc;
private boolean isDone;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
public boolean isDone() {
return isDone;
}
public void setDone(boolean isDone) {
this.isDone = isDone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"Todo [id=%s, user=%s, desc=%s, isDone=%s]",
id, user, desc, isDone);
}
}
\src\main\java\com\in28minutes\data\TodoRepository.java
package com.in28minutes.data;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.data.rest.core.annotation.RepositoryRestResource;
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "todos", path = "todos")
public interface TodoRepository
extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Todo, Long> {
List<Todo> findByUser(@Param("user") String user);
}
POST to http://localhost:8080/todos
Use Header => Content-Type:application/json
Request:
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false
}
Response:
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false,
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
}
{
"_embedded" : {
"todos" : [ {
"user" : "Jill",
"desc" : "Learn Hibernate",
"done" : false,
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
} ]
},
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos"
},
"profile" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/profile/todos"
},
"search" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/search"
}
},
"page" : {
"size" : 20,
"totalElements" : 1,
"totalPages" : 1,
"number" : 0
}
}
{
"user" : "Jill",
"desc" : "Learn Hibernate",
"done" : false,
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
}
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems http://projects.spring.io/spring-cloud/
COMING SOON
- What is Cloud?
- Why Cloud?
- Features of Spring Cloud
- Configuration management
- Service discovery
- Circuit breakers
- API Gateway
- Routing
Projects
- Spring Cloud Config
- Spring Cloud Netflix : Integrates with Netflix OSS components (Eureka, Hystrix, Zuul...)
- Spring Cloud Security : OAuth2 rest client support.
- Spring Cloud Data Flow : Orchestration service for microservice. Create microservice based data pipelines using
- DSL
- Drag-and-drop GUI
- REST-APIs
- Cloud Native Applications vs Micro Services
- Dynamic deployment to cloud needs a lot of automation
- Spring Boot Starter Project
- Its still a young evolving set of projects. Experience of Netflix is surely a good thing.
A lightweight, comprehensive batch framework designed to enable the development of robust batch applications vital for the daily operations of enterprise systems. http://projects.spring.io/spring-batch/
Coming Soon
- Restartability : Easy to restart a batch program from where it failed
- Different Readers and Writers : Provides great support to read from JMS, JDBC, Hibernate, iBatis etc. It can write to JMS, JDBC, Hibernate and more.
- Chunk Processing : If we have 1 Million records to process, these can be processed in configurable chunks (1000 at a time or 10000 at a time).
- Easy to implement proper transaction management even when using chunk processing.
- Easy to implement parallel processing. With simple configuration, different steps can be run in parallel.
A Job in Spring Batch is a sequence of Steps. Each Step can be configured with
- next : next step to execute
- tasklet : task or chunk to execute. A chunk can be configured with a Item Reader, Item Processor and Item Writer.
- decision : Decide which steps need to executed.
A Job Launcher can be used to execute a Spring Batch Job. A job can be launched/scheduled in a web container as well.
- Each execution of a job is called a Job Instance. Each Job Instance is provided with an execution id which can be used to restart the job (if needed).
- Job can be configured with parameters which can be passed to it from the Job Launcher.
<job id="job1">
<split id="split1" task-executor="taskExecutor" next="step4">
<flow>
<step id="step1" parent="s1" next="step2"/>
<step id="step2" parent="s2"/>
</flow>
<flow>
<step id="step3" parent="s3"/>
</flow>
</split>
<step id="step4" parent="s4"/>
</job>
For Batch Programs
- Be careful about Exception Handling and Transaction Management
- Be as near to data as possible
- Allocate enough memory
- Stress test from the start of the project. Identify production data volumes and evolve the application to meet those needs.
Spring Batch 3.0 supports JSR-352 -java specification for batch processing
Quick Start for Spring Projects. http://start.spring.io/
Coming Soon....
- Choose Maven or Gradle
- Choose Version of Spring Boot
- Add all the stuff you want!
- Download the project
- Run... Thats it!!!
- Awesome and Simple way to create Spring Boot Projects
- Supports more than 50 different frameworks
- Lets do a quick demo!
- Start of a project or when you want to do a quick prototype
Authentication and Authorization framework. (What is Authentication?) http://projects.spring.io/spring-security/
Coming Soon..
- Great support for authentication and authorization
- Provides out of the box support to prevent session fixation, clickjacking and XSS
- Integrates well with Spring and Spring Boot Projects
- Proven Framework. You do not want to play with Authentication and Authorization.
- Great Integration with wide range of technologies
- HTTP BASIC authentication headers
- HTTP X.509 client certificate exchange
- LDAP
- Form based
- JAAS
- org.springframework.security:spring-security-web
- Or use the spring security starter project!
Lets do a quick demo...
Spring support for HATEOAS (Hypermedia as Representation of Application State) http://projects.spring.io/spring-hateoas/
- Create services that include HATEOAS links in the response..
- Create clients for services using HATEOAS
Coming Soon
- Dynamic provisioning of resources (computing, network, servers, applications) on need.
- Imagine a startup. Do you know how fast you will grow?
- Imagine a shopping company. Do you really need all the infrastructure you bought planning for the peak period (Black Friday, Holiday Season) during the lean periods of the year?
- Imagine applications for businesses have a year end peak period. What would the infrastructure be doing rest of the year?
- Private
- Public
- Agility
- Cost reductions
- Scalability and elasticity
- Reliability
- Make sure your applications are Cloud Native
- Choose a platform
- Microsoft Azure
- AWS
- Google's Cloud Platform
- 12 factor apps
- Security
- Application Compatibility
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- PAAS (Platform as a Service)
- SAAS (Software as a Service)
Coming Soon
- Large volumes of data
- Few dozen terabytes to many petabytes of data
- Data Sources
- Social Networking - Facebook, Twitter
- Cameras
- Software Logs
- Faster, more intelligent decisions
- Business Trends
- Different Parts
- Capture
- Storage & Transfer
- Search
- Analysis
- Visualization
The Apache Hadoop software library is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high-availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures. Modules
- Hadoop Common: The common utilities that support the other Hadoop modules.
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS™): A distributed file system that provides high-throughput access to application data.
- Hadoop YARN: A framework for job scheduling and cluster resource management.
- Hadoop MapReduce: A YARN-based system for parallel processing of large data sets
Coming Soon
- Keep it Small - Small methods, Small classes, Small Components, Small Services, Small Deployable Units.
- Microservices are another step in the direction of “Keep it Small”. Fundamental change is to keep the deployable unit small.
- Many organizations found that embracing fine-grained, microservice architectures enable delivering software faster and adapt to new technologies.
- Evolved from on the ground experiences at Netflix, eBay, Amazon, Groupon
- Small, Lightweight
- Loosely coupled service-oriented architectures with bounded contexts
- Bounded Scope, Limited Scope, Solve one problem well
- Interoperable with message based communication
- Independently deployable and testable services
- Building systems that are replaceable over being maintainable
- Smart endpoints and dump pipes
- When you are having problems taking your releases live!
- Faster Time To Market
- Experimentation and Speed of innovation
- Team Autonomy
- Independent Teams
- Scaling
- High Tuning Ability
- Identifying the right bounded contexts
- Challenges due to change in thinking towards event driven architectures
- Increased need for Automation
- More complex Monitoring & Application health management
- Fault Isolation
- Correlation Ids
- Eventual Consistency through Standardization
- Need to decide what you want to standardize and what you do not want to standardize.
SOA started with similar aims. Let’s highlight a couple of significant differences.
- However, as time passed, SOA is characterized by large product based implementations arounds ESBs. These ESBs became the magnet for all business logic and over a period of time became the bottleneck.
- Microservices approach place additional focus on microservices being autonomous and independently deployable.
- Spring Boot
- Spring Cloud
Coming Soon
Applications which are easily deployable on cloud.
- Visibility
- Fault Isolation
- Fault Tolerance
- Automated Recovery
- DevOps
- Continuous Delivery
- Microservices - Bounded Context & Choreography
- Containerization
- 12 factors app
- Codebase - One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys
- Dependencies - Explicitly declare and isolate dependencies
- Config - Store config in the environment
- Backing services - Treat backing services as attached resources
- Build, release, run - Strictly separate build and run stages
- Processes - Execute the app as one or more stateless processes
- Port binding - Export services via port binding
- Concurrency - Scale out via the process model
- Disposability - Maximize robustness with fast startup and graceful shutdown
- Dev/prod parity - Keep development, staging, and production as similar as possible
- Logs - Treat logs as event streams
- Admin processes - Run admin/management tasks as one-off processes
###12 Factor App A methodology for building modern, scalable, maintainable software-as-a-service apps. Originated from developers at Heroku.
Coming Soon
- Best practices for Cloud native applications.
- 12 factors app
- Codebase - One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys
- Dependencies - Explicitly declare and isolate dependencies
- Config - Store config in the environment
- Backing services - Treat backing services as attached resources
- Build, release, run - Strictly separate build and run stages
- Processes - Execute the app as one or more stateless processes
- Port binding - Export services via port binding
- Concurrency - Scale out via the process model
- Disposability - Maximize robustness with fast startup and graceful shutdown
- Dev/prod parity - Keep development, staging, and production as similar as possible
- Logs - Treat logs as event streams
- Admin processes - Run admin/management tasks as one-off processes
- Cloud Native Applications
Microservices With Front-End
Coming Soon
- Backend teams can't deliver business value without the frontend being updated
- Needs communication between frontend and backend teams
A new approach to developing microservices, with both front-end and back-end included.
- Easy to take live - since only one microservice needs to be deployed
- One team works end to end!
- How to make sure that the individual frontends are consistent. Common Framework is an option. However the risk is the coupling a common framework might create
- Different UIs for different devices - Computer, Mobile, iPad etc..
Coming Soon
- Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State.
- One of the important constraints of REST application architecture.
- Any REST service should include contextual hypermedia links with the response.
{
"_embedded" : {
"todos" : [ {
"user" : "Jill",
"desc" : "Learn Hibernate",
"done" : false,
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
} ]
},
"_links" : {
"self" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos"
},
"profile" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/profile/todos"
},
"search" : {
"href" : "http://localhost:8080/todos/search"
}
},
"page" : {
"size" : 20,
"totalElements" : 1,
"totalPages" : 1,
"number" : 0
}
}
XML Example
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<account>
<account_number>12345</account_number>
<balance currency="usd">100.00</balance>
<link rel="deposit" href="https://somebank.org/account/12345/deposit" />
<link rel="withdraw" href="https://somebank.org/account/12345/withdraw" />
<link rel="transfer" href="https://somebank.org/account/12345/transfer" />
<link rel="close" href="https://somebank.org/account/12345/close" />
</account>
- Less Coupling with URI Structures
- HAL (Hypertext Application Language) is a simple format that gives a consistent and easy way to hyperlink between resources in your API.
- Resources have:
- Links
- Embedded Resources - other resources contained within them
- State - the actual resource data
- Links have:
- A target (a URI)
- A relation (a name)
Example
{
"links": {
"self": { "href": "http://api.com/items" },
"item": [
{ "href": "http://api.com/items/1" },
{ "href": "http://api.com/items/2" }
]
"data": [
{"itemName":"a"},
{"itemName":"b"}
]
}
Should be driven with an Example!
Should be driven with an Example!
- IMDB or MMDB
- Main memory used as primary storage
- In unit testing scenarios, you do not want to depend on external resources like a database. In memory databases help us to launch a database in memory, populate the data, run the tests and verify the results.
- Quick Prototyping and Learning
- Typically support a subset of the SQL (Structured Query Language) standard.
- Browser based console
- Include a jar
- Point your datasource to the url
- Database is automatically created
- Quick demo - Spring JDBC Example?
- Load one page and dynamically update the page on user actions.
- Provides user experience similar to a desktop application.
- Typically use AJAX and HTML5
- Complete page is never reloaded!
- http://demos.telerik.com/kendo-ui/websushi
- Gmail, Twitter and Facebook!
Typical architectures involve
- Building REST Services in the background! Java(most popular Spring Boot) or NodeJs
- Front-ends developed with frameworks like AngularJS, Ember.js, Meteor.js, ExtJS and React
- Improved User Experience
- Reduced load on servers because only parts of page are reloaded
- Leads to more microservice based architectures!
- Needs completely different mindset!
- Start developing a quick app with AngularJS with a stubbed/mocked backend!
Why duplicate? Reuse existing video?
- Cost of not using the best possible design and standards.
- Or how much cost is involved in getting to a good design meeting all standards
- Martin Fowler "extra effort that we have to do in future development because of the quick and dirty design choice"
- Impossible to measure accurately
- First thing: It cannot be measured perfectly! How do you find the technical debt because of wrong choice of technology, lack of common components, bad variable or method names.
- SonarQube - http://docs.sonarqube.org/display/SONARQUBE52/Technical+Debt
- Measures technical debt against different Non Functional Requirements! Gives a SQALE rating!
As the application becomes bigger, the productivity of the team goes down. You would notice that the velocity of the team comes down.
- Simple Architecture (4 Principles of Simple Design)
- Continuous Refactoring
- Good Unit Tests
- TDD
- Static Analysis
- Good Standards
- Peer Reviews
- Fingers crossed (Nobody can predict future architecture and when current architecture becomes obselete)
- Maintain a Technical Backlog
- Do a cleanup spring once in a while!
- How do you improve a project which already has a large Technical Debt?
- Identify potential areas of improvement
- Identify changes in the next 6 months
- Write test for areas which are gonna be changed in the next 6 months
- Refactor
- Build the test base over a period of time
- Have Technical Debt as part of Definition of Done
- Measure Technical Debt from day one of the project!
How much percentage of your source code is covered by unit tests?
http://www.sonarqube.org/manage-code-coverage-by-unit-tests-with-sonar/
- Unit Testing is one of the most important modern development practices.
- Good Unit Tests are there for ever! They catch defects in future!
- Systems with good unit tests improve over a period of time! Developers are not worried about breaking functionality. So, they continuously refactor!
- Not having proper asserts
- Writing tests just for coverage!
- Certains parts of the applications are not designed for unit testing
- Old frameworks - Web and database especially
- SONAR
- Eclipse - Cobertura and EclEmma plugins
- Inbuilt in Intellij
- Have Code Coverage as part of Definition of Done
- Measure Code Coverage from day one of the project!
Unit Testing Dependency Injection In memory databases
Make your choice
- Old Code!
- Code without Tests?
- Code with Lot of Technical Debt?
- Code with old out of date frameworks and languages?
- Unexpected impact - Changing one part of application impacts another part
- Large code bases
- Large teams
- Long Release Cycles
- Refactor (atleast very important areas)
- Replace :)
- Have good code review process
- Introduce Static Analysis where possible
- Introduce Unit Testing where possible
- Measure Technical Debt
- Have Automated Regression Tests at least
- Especially as writing good unit tests might be difficult
- Develop new functionality outside using new architecture and connect using services
- Refactoring
- Code Quality
- Lets not worry about it!
In water fall model, we followed an approach where we architected and designed the entire system before we started coding. Evolution Design is using a combination of good tests and high level architecture base to drive you to a good design. You apply basic design principles (4 Principles of Simple Design) and continuously refactor your code ensuring good design emerges. Uses an iterative approach. At each pass - add, refactor and test
- Avoids over design
- Avoids designing for some future feature which never materializes
- Continuous & Immediate feedback as we are not waiting for all design to complete before we deliver value to customer
- Need clear separation between Design and Architecture
- Need skilled and experienced developers/architects to guide and govern
- Needs Continuous Integration
- Needs high focus on tests. If tests are not good, design cannot evolve as developers are reluctant to make changes!
- Use TDD
- Use Continuous Integration
- Good Question. Experience it to learn it. Pair with Good Programmers.
When we develop any service, we have two approaches
- Code First
- Contract First
In Code First approach we write the code for the service first and generate the contract for the service from code!
Swaggerizing Spring Boot Services Generating WSDL from Web Service Code
Exposing Swagger contract from REST Services
- Does not need additional effort to create the contract!
- Contract and Code always in sync!
- Makes it difficult to develop in parallel!
- Teams do not know the target! As contract is not agreed ahead of time, teams might make more changes than necessary.
- In old frameworks, sometimes the generated contract was not compatiable across platforms!
- How do we support versioning?
- Makes it more difficult to make a choice
- Tools are evolving. Today some of the disadvantages of Code First have alternatives.
When we develop any service, we have two approaches
- Code First
- Contract First
In Contract First approach we agree on the contract for the service first. We write code based on the contract.
- Teams can develop in parallel!
- Teams know what to expect. Can use some stub framework to mock the service based on the contract.
- Cross Platform Compatible
- Enables reuse of Schemas
- Some initial additional effort
- Needs some effort to ensure that the updated contracts are shared as when needed
- Makes it more difficult to make a choice
- Tools are evolving. Today some of the disadvantages of Code First have alternatives.
- Everything on the web is a web service!
- Fundamental to SOA and Microservice approaches.
- Service Provider : Google.com is the service provider. Handles the request and sends a response back.
- Service Consumer : Browser is the service consumer. Creates Request. Invokes Service. Processes the Response.
- Data Exchange Format : In this example, Data Exchange is done over HTTP protocol. Request is HTTP request and Response is HTTP Response. Data exchange format can be something else as well. XML (in case of SOAP web services) and JSON (most RESTful services).
- Contract : Agreement to the definition of a service.
- SOAP : Simple Object Access Protocol
- REST : RESTful Web services
- Re-use : Web services avoid the need to implement business logic repeatedly. If we expose a web service, other applications can re-use the functionality
- Modularity : For example, tax calculation can be implemented as a service and all the applications that need this feature can invoke the tax calculation web service. Leads to very modular application architecture.
- Language Neutral : Web services enable communication between systems using different programming languages and different architectures. For example, following systems can talk with each other : Java, .Net, Mainframes etc.
- Web Services are the fundamental blocks of implementing Service Oriented Architecture in an organization.
- Contract First vs Code First
- SOAP vs REST
- REST is winning the race. Lightweight. With JSON, more options for consumers.
- HTTP vs JMS vs AMQP vs...
- As we move towards Microservices with event driven architectures, AMQP is getting more popular as a means of programming language neutral asynchronous communication approach.
- Defining Contracts
- WSDL for SOAP Services
- Swagger/RestDocs for RESTful JSON Services
- Keep your contracts programming language neutral
- Follow contract first
- JSON based RESTful services are emerging as a popular approach. They are lightweight and consumable from browser and mobile apps.
- Let run a web service and call it using Postman?
- Refer web service section above for understanding what a web service is.
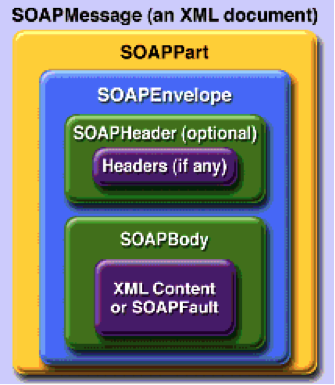
- In SOAP web services, data exchange (request and responses) happens using SOAP format. SOAP is based on XML.
- SOAP is a platform independent messaging protocol. Allows communication between disparate operation systems. For example, a system using Windows can talk to as sytem using UNIX using services built using SOAP protocol.
- SOAP format defines a SOAP-Envelope which envelopes the entire document. SOAP-Header (optional) contains any information needed to identify the request. Also, part of the Header is authentication, authorization information (signatures, encrypted information etc). SOAP-Body contains the real xml content of request or response.
- All the SOAP web services use this format for exchanging requests and responses. In case of error response, server responds back with SOAP-Fault.
- Define a Contract
- Create Service Provider
- Create Service Consumer
Request/Response Client Side Server Side Request (1)Java Object => SOAP Request XML ----o-------> (2)SOAP Request XML => C# Object Response (4)Java Object <= SOAP Response XML <----o----- (3) SOAP Response XML <= C#Object
- Structure of Request and Response XML are defined in WSDL
- Converting Java object to SOAP xml. This is called Marshalling.
- Converting SOAP xml to Java object. This is called Unmarshalling. JAXB and XMLBeans are frameworks which enable use to do marshalling and unmarshalling easily.
- At transport level, SSL is used to exchange certificates (HTTPS). This ensures that the server (service producer) and client (service consumer) are mutually authenticated. It is possible to use one way SSL authentication as well.
- At the application level, security is implemented by transferring encrypted information (digital signatures, for example) in the message header (SOAP Header). This helps the server to authenticate the client and be confident that the message has not been tampered with.
- Let run a web service and call it using Postman?
- There are a set of architectural constraints called REST Constraints. Any service which satisfies these constraints is called RESTful Web Service.
- There are a lot of misconceptions about REST Web Services : They are over HTTP , based on JSON etc. Yes : More than 90% of RESTful Web Services are JSON over HTTP. But these are not necessary constraints. We can have RESTful Web Services which are not using JSON and which are not over HTTP.
The five important constraints for RESTful Web Service are
- Client-Server : There should be a service producer and a service consumer.
- The interface (URL) is uniform and exposing resources. Interface uses nouns (not actions)
- The service is stateless. Even if the service is called 10 times and there is no change in the state of the resource, the result must be the same.
- The service response should be Cacheable.
- Client should not assume direct connection to server - it might be getting info from a middle layer - cache.
-
HTTP is the protocol to exchange or transfer hypertext.
-
Request–Response protocol
-
HTTP Request - The request message consists of the following:
-
A request line with request method and URI (e.g., GET /images/logo.png HTTP/1.1, which requests a resource called /images/logo.png from the server).
-
Request header fields (e.g., Accept-Language: en).
-
An optional message body.
-
HTTP Response - The response message consists of the following:
-
A status (e.g., HTTP/1.1 200 OK).
-
Response header fields (e.g., Content-Type: text/html).
-
An optional message body.
-
HTTP methods: indicate the desired action to be performed on the identified resource. GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE among a host of others.
-
Different HTTP Status Codes
- While designing any API, the most important thing is to think about the api consumer i.e. the client who is going to use the service. What are his needs? Does the service uri make sense to him? Does the request, response format make sense to him?
- Always use HTTP Methods. Best practices with respect to each HTTP method is described below:
- GET : Should not update anything. Should be idempotent (same result in multiple calls). Possible Return Codes 200 (OK) + 404 (NOT FOUND) +400 (BAD REQUEST)
- POST : Should create new resource. Ideally return JSON with link to newly created resource. Same return codes as get possible. In addition : Return code 201 (CREATED) is possible.
- PUT : Update a known resource. ex: update client details. Possible Return Codes : 200(OK)
- DELETE : Used to delete a resource.
- Have properly structure URIs. URI’s should be hierarchical and as self descriptive as possible. Prefer plurals.
- Friends List - GET /users/Ranga/friends
- Add a Friend - POST /users/Ranga/friends
- Get details about a specific friend - GET /users/Ranga/friends/Ravi
- JAX RS
- Spring MVC
JAX-RS is the JEE Specification for Restful web services implemented by all JEE compliant web servers (and application servers). Important Annotations
- @ApplicationPath("/"). @Path("users") : used on class and methods to define the url path.
- @GET @POST : Used to define the HTTP method that invokes the method.
- @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) : Defines the output format of Restful service.
- @Path("/{id}") on method (and) @PathParam("id") on method parameter : This helps in defining a dynamic parameter in Rest URL. @Path("{user_id}/followers/{follower_id}") is a more complicated example.
- @QueryParam("page") : To define a method parameter ex: /users?page=10. Useful methods:
- Response.OK(jsonBuilder.build()).build() returns json response with status code.
- Json.createObjectBuilder(). add("id",user.getId()); creates a user object.
- Swagger
- Restdocs
Richardson Maturity Model defines the maturity level of a Restful Web Service. Following are the different levels and their characteristics.
- Level 0 : Expose SOAP web services in REST style. Expose action based services (http://server/getPosts, http://server/deletePosts, http://server/doThis, http://server/doThat etc) using REST.
- Level 1 : Expose Resources with proper URI’s. Ex: http://server/accounts, http://server/accounts/10. However, HTTP Methods are not used.
- Level 2 : Resources use proper URI's + HTTP Methods. For example, to update an account, you do a PUT to . The create an account, you do a POST to . Uri’s look like posts/1/comments/5 and accounts/1/friends/1.
- Level 3 : HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the engine of application state). You will tell not only about the information being requested but also about the next possible actions that the service consumer can do. When requesting information about a facebook user, a REST service can return user details along with information about how to get his recent posts, how to get his recent comments and how to retrieve his friend’s list.
- Have a RESTful api standard across organization- YARAS
- Message and URI Layout, HATEOAS, Sorting, Filtering, Pagination
- Use HATEOAS where possible
- Have Great Unit Tests!
- Show case a Spring MVC Based REST Service
- Show case HATEOAS
- Show case Swagger Documentation
- Isn't this already done?
- We want to build a large application talking to multiple services. When we start developing an application, we want to lay down the architecture and design, set up frameworks, integrate them and setup unit testing.
- Vertical Slice can be a small use case which ensures all layers are involved
- Database
- External Services
- Vertical Slice is used to identify and solve technology risks at the very start of a project.
- Vertical Slice acts as a reference for other developers as they start building more stuff.
- Ensure that Static Analysis is in place in parallel and Vertical Slice adheres to all standards
- Ensure that continuous integration is in place.
- Do developers need trainings on the frameworks?
- Identify the right use case for the vertical slice! Usually choose a relatively complex use case!
Customizing an application for use in different locations and languages - for different Locales!
- You don't want 100 applications for 100 Locales
- Lets take a quick demo of implementing it with Spring MVC!
- Sometimes data from database tables need to be internationalized. This needs a custom solution.
Build it in from the first day. Should be part of vertical slice usually.
- Already done!
Requirements which are not typically specified as part of how application should behave
- Authentication and Authorization
- Performance
- Scalability
- Availability
- Resilience
- Maintainability
- Portability
- Security
- Have clearly stated non functional requirements
- Build vertical slices where-ever possible to eliminate most important non functional risks - scalability or performance
- Will the framework be able to withstand a specific load?
- Check for Security from start of the project.
- Use Static Analysis from start of the project.
- Use Secure Code Static Analysis tools from start of the project.
- Sometimes you do not know the target for non functional requirement? What if your app becomes more popular than what you expect?
- Authentication: Are you who you state you are?
- Authorization: Do you have access to the specific resource or functionality?
- Use HTTPS - SSL
- Use Standard Frameworks - Spring Security
- Authorization: Have a clear framework. Check before performing action. Best way to implement is to use Filters
- Use Server Side Validations.
- Don't re-invent the wheel.
- Don't allow your access tokens to last forever.
- Don't store access tokens or passwords in plaintext.
- Build visibility into volumes of authentication failures.
- Do not use Basic Authentication
- Use secure cookies only
How fast is your application?
- Have clear performance objectives
- Make the right architecture choice for your needs
- If needed, implement a vertical slice quickly to test performance
- Measure Early
- Use Load Tests early in the cycle
- NO premature optimizations. Any optimization decision should be based on numbers or past experience. In Donald Knuth's paper "Structured Programming With GoTo Statements", he wrote: "Programmers waste enormous amounts of time thinking about, or worrying about, the speed of non critical parts of their programs, and these attempts at efficiency actually have a strong negative impact when debugging and maintenance are considered. We should forget about small efficiencies, say about 97% of the time: premature optimization is the root of all evil. Yet we should not pass up our opportunities in that critical 3%."
- Session size - Small
- Implement Caching where ever possible
- Create necessary Indexes on Database. Collect Statistics and Remove unnecessary data
- In critical parts - write unit tests for performance.
- Java Specific
- Set initial size on Collections
- Be conscious about create as few objects as possible. Especially in loops.
- Avoid String Concatenation
- Eliminate Obselete Object References
- Close connections and Streams
- Will your system handle more load if you give it more resources?
- "A system whose performance improves after adding hardware, proportionally to the capacity added, is said to be a scalable system."
- If supporting X users needs Y resources, will I be able to support 2X users or better with 2Y resources?
- Horizontal : Add more nodes to cluster. Now popular with the cloud bringing in new possibilities.
- Vertical : Add resources to the current node. Increase main memory, for example.
- Comparison
- There are limits to how much you can scale vertically.
- Usually databases become the bottleneck in large systems.
- Have clear scalability targets
- Test Early
- Be wary of typical bottlenecks - Things which are difficult to scale horizontally
- Load balancers
- Databases (Do not have a large database! Try splitting up databases! Transaction database, Reporting database. See if you can have as small databases as possible)
- Large Monolithic Application (difficult to deploy!)
- Caching can improve scalability
- Static Resources
- Configuration Data
- User Data
- Service Responses
- Think of a Distribute Cache
- Build visibility and build alerts
- Build cloud native microservice based applications and make use of the cloud!
- Proportion of time that the system is functional and working
- Downtime can be caused by
- Software Errors
- Infrastructure Problems
- Denial of Service Attacks
- High Load
- Examples
- High load on database
- A server crash because of a bug in code
- Build Redundancy
- Identify possible bottlenecks or choke points and plan to reduce them
- Install Security Updates of Operating System and Software
- Load Test with real time loads
- Have proper exception handling
- Have Automated Visibility to detect unusual patterns.
- Validate data on the Server
- How does your system respond in case of a failure of a specific component or a service?
- Can it provide reduced set of functionality instead of completely breaking down?
- Especially important in the world of microservices. Things become more distributed increasing the chances of failure
- Will the entire amazon.com be down if product recommendations service is down?
- Always think what if a service is down?
- Test for service failures. Switch off a service and see how the system reacts
- Use Circuit Breaker Frameworks like Hystrix
- How is easy is it to make changes to your system?
- How frequently do things break when you make a change?
- How many defects come as a result of changes?
- How much effort does it take to make a change?
- Coding Standards, Static Code Analysis and Peer Reviews
- Loose Coupling and High Cohesion
- Proper Layering
- Small Applications compared to Monoliths
- Continuous Integration
- Automation Testing - Unit Testing and Integration Testing
- Sufficient Documentation
- How easy is it to move other Language, Database, Framework or a Platform?
- How easy can you move from Hibernate to other framework? JPA
- How easy can you move from Websphere to Weblogic? Adhere to JEE standards
- How easy to move from Windows to Unix? If you have a java based application, you already made a good start
- How easy is to move from Oracle to mySql? Are you adhering to Ansi SQL Standards? Are you using any Oracle specific features?
- How easy is to test parts/components of your application?
- Avoid Monoliths
- Too much business logic. Too difficult to test.
- Simple Design using Dependency Injection
- Design for Testability
- Agreed contacts for Services
- Architectures build with development needs - Stubs & Mocks
- Focus on Unit testing and Integration testing from the first day of the project
- Use TDD and Continuous Refactoring
- Protect from unintended use!
- Protect from denial of service attacks.
- Protect unauthorized users from gaining access
- Restrict authorized users access only to the specific modules or data they are supposed to access!
- Least Priviliges : Build with security in mind from the initial project stages. Think about various user roles and accesses
- Complete Mediation : Similar to building a security for a King's fort. One Gate through which every body has to pass through. Ex: Spring Security
- Defence in Depth : Have Multiple levels of security.
- Trust Nothing
- Validate all data into system.
- Sanitise data
- Economy of Mechanism. Keep it simple. Simple systems are easy to protect
- Openness of Design
- Opposite to "Security through Obscurity"
- Prevention
- Detection
- Reaction
- Think of security from day one
- Educate developers, testers, operations teams and business about the threats
- Be aware of OWASP and their recommendations
- Test Early
- Use Security Static Analysis tool
- Get external security testers to hack your applications!
- OWASP
- Have an approved software/framework/platfrom list by a Security Team
- Use latest versions
- Safeguard web server, app server, os & hardware.
- Web sphere admin console example - Deleting default accounts & Exposing it outside enterprise.
- Use encryption for sensitive data. One way functions. When hashing use some salt - Salt can be stored in Db for each user.
Injecting a part of query through a form field!
- LDAP
- XML Xpath
- Log
- OS Command
- XSS (Javascript)
- Parameterised Queries
- Invalid Data
- external services
- databases
- user
- Stored : Stored in db from ui. Problem happens when info is shown to user at a later point.
- Reflected : Dom - Untrusted data processed in JavaScript
- Stealing Session Cookies
- Page Content Rewrite
- Logging Keystrokes
- Validate untrusted data
- Encode all data - even trusted data
- Encoding should be contextual
- CSS
- HTML
- JS
- Ideally contextual encoding should be built into the frameworks
- Use JSTL & Other tag libraries
- Use Content Security Policy
- XSS Prevention Cheat Sheet
User changes link on the browser from resource he has access to to one which he has no access to
- /account/123 to /account/125
- especially vulnerable if the reference appears in url
- Proper Authorization using Mediation - Filters
- Use object references in urls
- Avoid predictability of urls
- things that can be compromised in non secure request
- passwords
- session ids
- Other sensitive data on page
- Use TLS
- All elements on page should use TLS
- Popups
- Other websites we redirect to
- Possibility of sending session id cookie insecurely to a NON https website redirect
- Use Secure Cookies : Mark cookies as secure. These are sent only to secure (https) websites
- Use Trusted Certificates
- Reissue session tokens when switching between secure and insecure website pages
Reuse of an user's existing session on a banking website on a forum to fire a unauthorised url or ajax request
- I log into a banking website and go to a forum without logging out
- My session cookie is in my browser!! It can be abused
- Include an unpredictable UNIQUE token with every request called CSRF Protection token. typically a hidden form field
- Reauthenticate user when performing significant actions
- Use frameworks like OWASP CSRF Guard or Spring Security
- Http is stateless
- How to identify a user between subsequent requests
- Url Rewrite - Session id in url
- vulnerable to sniffing
- Url is logged in multiple places including web server logs
- When you visit a third party site, the url is sent as a REFERRAL URL in request header
- Recommendation: Use https for entire session
- Basic Authentication : Base 64 encoded userid and password in every request
- Sniffing
- NOT RECOMMENDED
- Cookies
- Use domain : which hosts should this cookie be sent to path
- Use expiration date
- Mark as secure : sent only to https websites
Improper Authorization
- Complete Mediation Principle
- Filters or interceptors
- Have well defined roles
- Changing url in browser
- Firing AJAX Requests
- OS level virtualization technology
- Shares the host operating system kernel
- No dedicated operating system
- Lightweight
- High performance
- TODO MORE
Copy Again~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Coming Soon
- Refer our TroubleShooting Guide - https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes-initiatives/tree/master/The-in28Minutes-TroubleshootingGuide-And-FAQ
in28Minutes is creating amazing solutions for you to learn Spring Boot, Full Stack and the Cloud - Docker, Kubernetes, AWS, React, Angular etc. - Check out all our courses here