English | 中文文档
Cache mechanism base on Web Worker, help us build high performance webApp.
👋 Type-Safer. Arrow Cache is written in TypeScript and good support for code hints and type constraints.
🚀 High performance. all operations on cache library is asynchronous, the reason is that behind it is Worker Thread that handle all the storage access operations.
🍰 Less memory. the cache items filter by simple and effective algorithm to ensure the proportion of hot data in memory.
🍷 Rich API. provide a series methods for manipulate the cache store to control the life-circle of cache item effective.
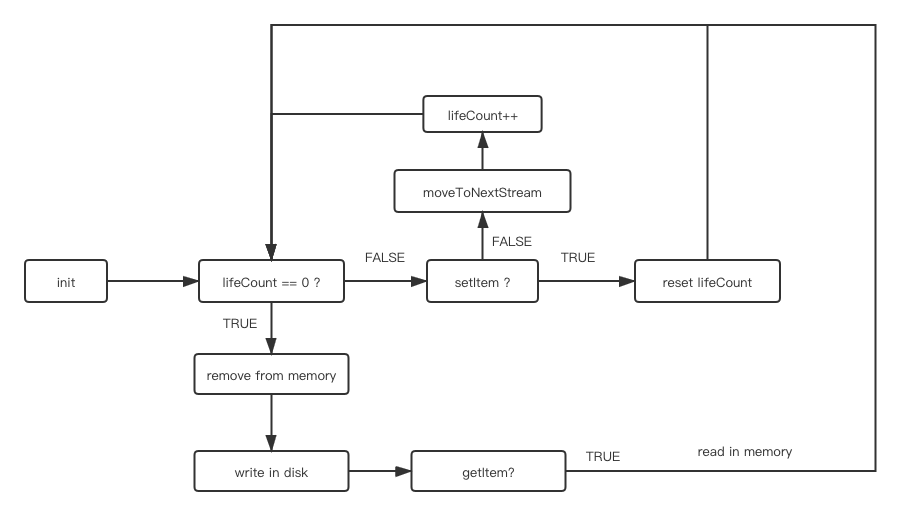
🌲Data persistence. Arrow Cache will remove it and from memory and persist it to disk if it's lifeCount eq to 0.If I access it again, it will be read in memory to improve speed for next access.
Arrow Cache use key-value to cache data like any other cache library. Any data stored in Arrow Cache will be put into memory immediately.But the amount of data you put in is proportional to the amount of memory you use, Arrow Cache will create a timer to mark-clean at regular interval for keep hot data in memory.The marked data will be persist in disk and remove it in memory. Arrow Cache will quest this data in memory first when access it next time, if not found, Worker will create a IO request to look for it from the disk, and if found it, this data will be read in memory and initialize.
Each data store in Cache store has a isActive tag and lifeCount tag.
isActive
Data is active when it already in memory, in this case, the isActive of this data is TRUE. The isActive of this data will go from TRUE to FALSE if it is written to disk, in this case, this data is not active anymore.
lifeCount
LifeCount is core of mark-clean mechanism, Arrow Cache will check the lifeCount for each data in Cache Store is 0 (default is 2) at regular interval(default is 10min and can be change it by setting clearDuration option). Arrow Cache will mark this data as imminentDead to indicate that it can be cleared when the lifeCount of this data is 0, then Arrow Cache will persisted all data with imminentDead tag to disk.
# yarn
yarn add arrow-cache
# npm
npm install arrow-cache/** Usage */
import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
const cache = new ArrowCache();
cache.setItem("name", "Jon");ArrowCache(Options)
You can pass a options when create instance of ArrowCache. The available properties are as follows:
isPermanentMemory [Boolean]
Mark cache as "Permanent Memory". If the isPermanentMemory is true, Arrow Cache will persist the data in disk when you invoke setItem every time. And read it into memory when refresh the page next time. As a caller, you will feel that it's always in memory.
clearDuration [Number]
Set the cleaning circle. Arrow Cache will clear data which lifeCount is 0 at regular interval.
To avoid making redundant non-null assertion, We provide default values for individual method, for example:
import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
const cache = new ArrowCache();
// 👎
const doSomething = async () => {
const foo = await cache.getItem("foo");
if (!foo) {
cache.setItem("foo", 0);
}
// ...
};
// 👍
const doSomething = async () => {
const foo = await cache.getItem("foo", 0);
// ...
};
// 👍
const doSomething = async () => {
const foo = await cache.append("foo", foo => foo + 1, 0);
// ...
};Arrow Cache provide some methods to update the content of cache, for example, setItem and updateContent. We say setItem has side effect and updateContent has not side effect. setItem will create a new item in Cache Store when content of key does not exist. But updateContent will return false and is not automatically created a new item in the Cache Store. The other difference is setItem will mark this data as active and read in memory when the data is already written in disk and mark as hot data, but updateContent does not change the state of data whether the data is in memory or on the disk.
////////////////////////// SIDE EFFECT /////////////////////////
cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 0);
setTimeout(async () => {
console.info(await cache.snapshot()); // {memory: {}, disk: {foo: "0"}}
await cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 1);
console.info(await cache.snapshot()); // {memory: {foo: {content: "1", lifeCount: 2, isActivated: true}}, disk: {}}
}, 2100);
cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 0);
//////////////////////////// PURE ////////////////////////////
setTimeout(async () => {
console.info(await cache.snapshot()); // {memory: {}, disk: {foo: "0"}}
await cache.updateContent(CACHE_KEY, 1);
console.info(await cache.snapshot()); // {memory: {}, disk: {foo: "1"}}
}, 2100);Arrow Cache will read data into memory from disk by Worker Thread when create instance, This procedure initializes Arrow Cache.You can pass a callback to onInit if you want to do something after initializes Arrow Cache.
import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
const cache = new ArrowCache();
cache.onInit(() => {
// do something...
});Mastering life-circle of cache item can better control performance and current situation of the Cache.
We provide three APIs to help you control life-circle of cache item.
moveToNextStream(key: string): Promise<boolean>moveToNextStream can move cache item of key to next clear-circle. lifeCount is the only factor that influence whether the cache item is active. moveToNextStream will cause lifeCount of the item + 1 and move it to next clear-circle. But if moveToNextStream return false indicate that the item of key does not exist.
markAsActive(key: string): Promise<boolean>markAsActive can read the item of key in memory, the method will return false when the item of key does not exist.
markAsStatic(key: string): Promise<boolean>markAsStatic can write the item of ket on the disk, the method will return false when the item of key does not exist.
We provide a series methods that easily get all keys of the cache store.
activeKeys(): Promise<string[]>activeKeys return all keys of data in the cache, and also means that all cache item in memory is active.
staticKeys(): Promise<string[]>staticKeys return all keys of data on the disk, and also means that all cache item on the disk is not active.
keys(): Promise<string[]>keys return all keys of cache whether the data is in memory or on the disk.
Sometimes, we need to know situation of cache in memory, therefore we can print snapshot of cache by invoke snapshot method.
import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
const cache = new ArrowCache();
(async () => {
console.info(await cache.snapshot()); // {memory: {}, disk: {}}
})();snapshot method return snapshot of cache at current point in time. The snapshot method will return a new object that is a shallow-copy of memory.
We have some examples under the Examples, you can start the example by npx parcel index.html
import React, { useLayoutEffect, useState } from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
import { Count } from "./styles";
import { Logo, Global, Button, Container } from "../common";
const cache = new ArrowCache({
isPermanentMemory: true
});
const COUNT_KEY = "count_key";
const Counter = () => {
const [num, setNum] = useState(0);
const initNum = async () => setNum(await cache.getItem(COUNT_KEY, 0));
const increment = async () =>
setNum(await cache.append(COUNT_KEY, pre => pre + 1, 0));
useLayoutEffect(() => {
initNum();
}, []);
return (
<Container>
<Global></Global>
<Logo></Logo>
<Count>{num}</Count>
<Button onClick={increment}>increment</Button>
</Container>
);
};
render(<Counter />, document.querySelector("#root"));import { ArrowCache } from "arrow-cache";
import { Button } from "../common";
import React from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
const cache = new ArrowCache({
clearDuration: 1000
});
const CACHE_KEY = "foo";
const App = () => {
const handleSideEffectClick = () => {
cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 0);
setTimeout(async () => {
console.info(await cache.snapshot());
await cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 1);
console.info(await cache.snapshot());
}, 2100);
};
const handlePureClick = () => {
cache.setItem(CACHE_KEY, 0);
setTimeout(async () => {
console.info(await cache.snapshot());
await cache.updateContent(CACHE_KEY, 1);
console.info(await cache.snapshot());
}, 2100);
};
return (
<>
<Button onClick={handleSideEffectClick}>side effect</Button>
<p></p>
<Button onClick={handlePureClick}>pure</Button>
</>
);
};
render(<App />, document.querySelector("#root"));MIT.