Sometimes, it may be useful to be able to see how an HTTP cache or proxy modifies the traffic that passes through it. Use cases might include testing cache/proxy configurations (eg. Varnish VCL being applied), or evaluating how malformed requests are handled & forwarded.
This Vagrant environment facilitates the creation of a Varnish Cache test environment, wrapping it with pre-/post-cache MITM capabilities.
This creates a single virtual machine running Ubuntu Trusty 14.04 with:
- Varnish (front-end cache)
- lighttpd (back-end content server)
- Hitch (TLS termination)
- mitmproxy (HTTP/HTTPS man-in-the-middle)
It should be somewhat straightforward to swap out Varnish for some other cache or proxy component, if a different target needs to be tested.
Tested with VirtualBox 5.0 and Vagrant 1.7.4.
Varnish and Hitch are both pulled from their Github repositories and built from source, in order to get most recent versions.
Initially, the configuration deployed is as follows:
https-client http-client
| |
hitch:443 |
\ |
\ |
varnish:80
|
lighttpd:8080
Scripts are provided to reconfigure into a pre- and post-cache MITM flow, using mitmproxy running in reverse proxy mode:
https-client http-client
| |
hitch:443 |
\ |
\ |
mitmproxy:80
|
varnish:8081
|
mitmproxy:8082
|
lighttpd:8080
Running mitm-enable.sh will reconfigure Varnish in this mode.
Running 'screen -c wrapper-monitor.screenrc' will start a screen session, with mitmdump processes at both pre-cache and post-cache positions in the flow.
The commands in the screenrc that are run to initialize the two mitmdump processes could be modified, for example to run mitmproxy if the user wants interactive access to the MITMed flows.
Test HTTP/HTTPS requests can be generated from within the virtual machine itself, or from the host system by targeting the Vagrant-configured IP (192.168.200.2 by default). Keeping it simple, curl works in both cases, or a browser on the host system.
Running mitm-disable.sh will kill any remaining mitmdump processes and reconfigure Varnish to return the flow to original state.
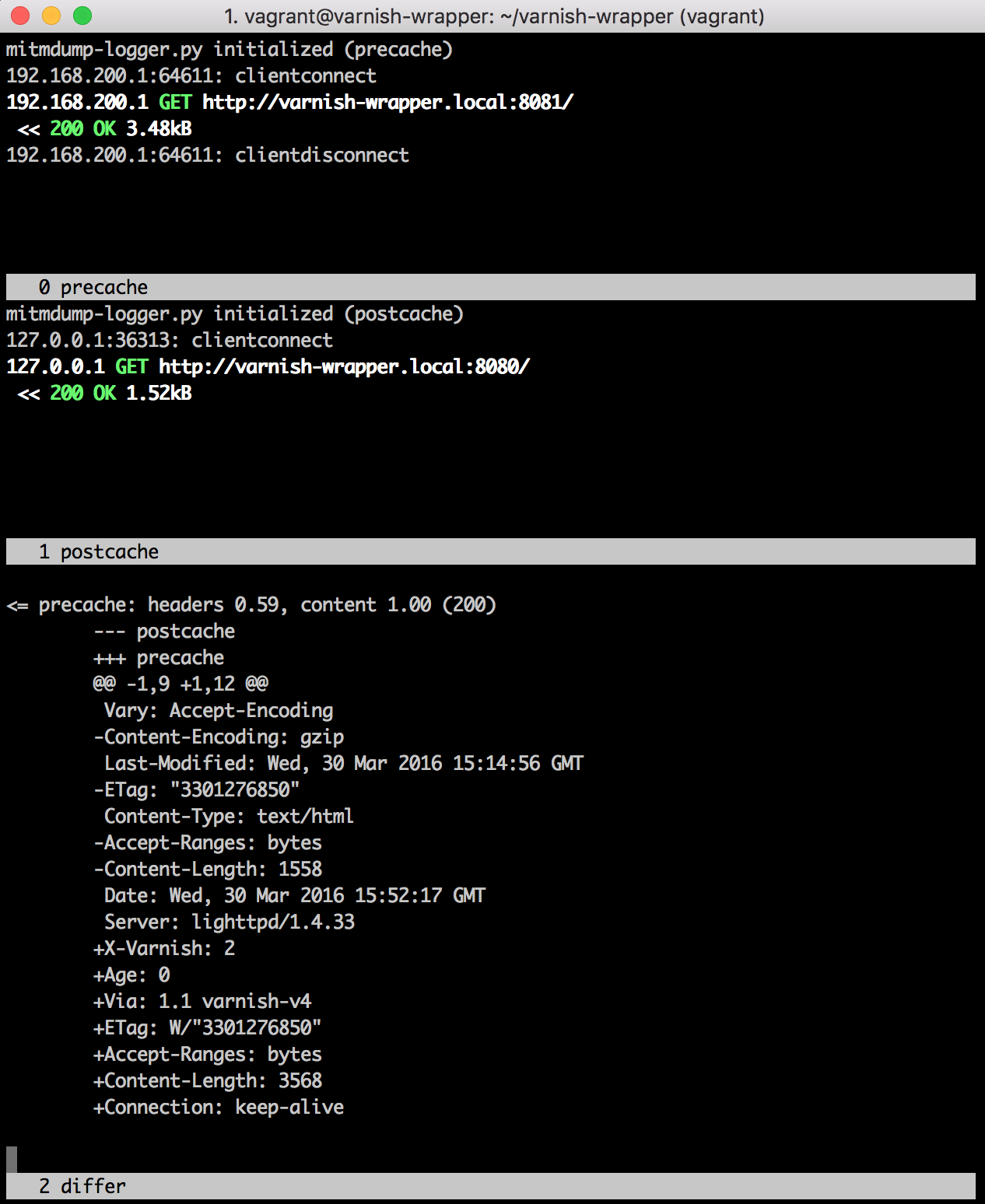
Running 'screen -c wrapper-diff.screenrc' will start a screen session, with mitmdump processes at both pre-cache and post-cache positions. It will also enable an mitmproxy script (mitmdump-logger.py) that uses header injection to tie pre-/post-cache requests to each other, and persist the requests/responses in an SQLite database.
Running analyze-flows.py will perform some basic analysis against the request/ response pairs in the SQLite database and indicate where differences are identified.
Logs for Hitch are dropped into the daemon syslog facility, which drop into /var/log/daemon.log on the system.
Logs for Varnish can be accessed by executing /opt/varnish/bin/varnishlog, which is documented at: https://www.varnish-cache.org/docs/4.1/reference/varnishlog.html