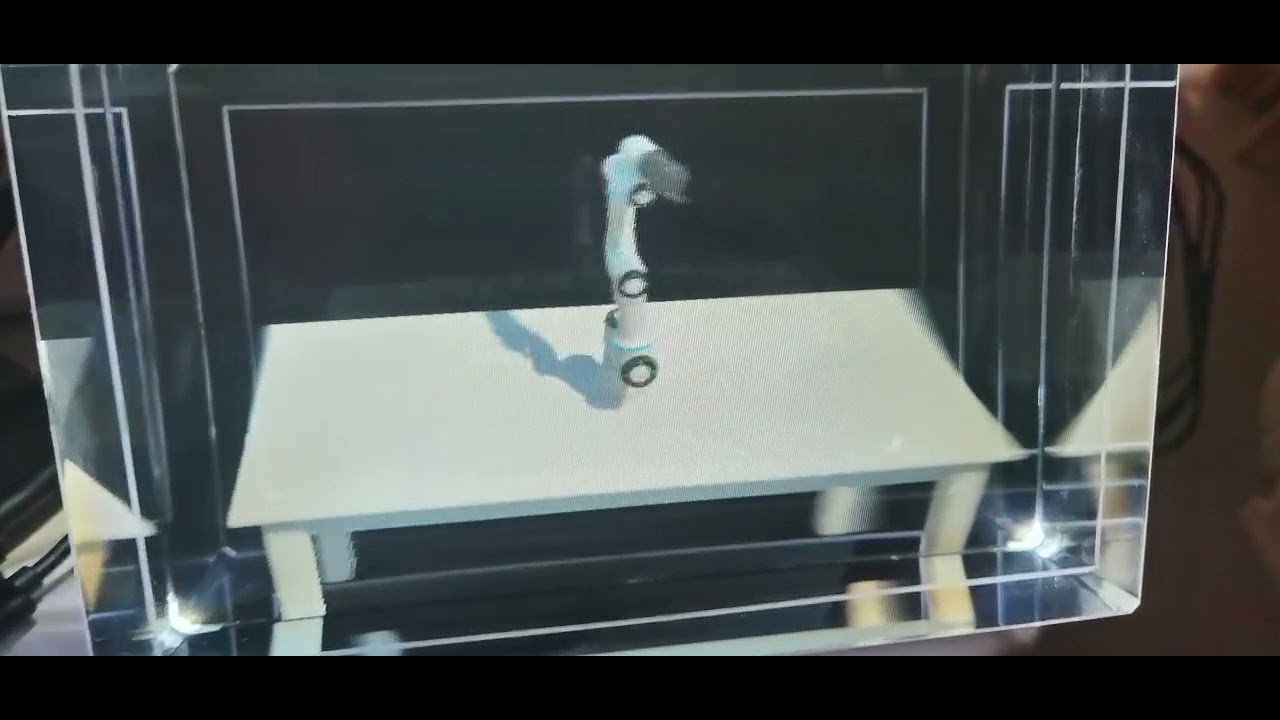
This is a simulation of the Universal Robotics UR3e robot using Unity's new articulation joint system.
This new joint system, powered by Nvidia's PhysX 4, is a dramatic improvement over the older joint types available in Unity. It uses Featherstone's algorithm and a reduced coordinate representation to gaurantee no unwanted stretch in the joints. In practice, this means that we can now chain many joints in a row and still achieve stable and precise movement.
Unity 2020.1.0b7 or later is needed for the new joint system. This UR3 demo works with ML-Agents Release 1 to demonstrate the UR3 learning to touch a cube.
To install this demo and experiment with the UR3 simulation and ML-Agents training you will need an appropriate version of Unity, a clone of this repo and the ML-Agents Toolkit.
If you do not have Unity 2020.1.0b7 or later, add the latest 2020.1 beta release through Unity Hub. This demo was last tested on Unity 2020.1.0b7.
Clone this branch of the repository:
git clone --branch mlagents https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/articulations-robot-demo`.Alternatively, you can clone the entire repo and checkout the mlagents branch:
git clone https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/articulations-robot-demo
git checkout mlagentsThe ArmRobot folder contains the ArticulationRobot scene. If you open the scene
in Unity you will see a few errors since the ML-Agents package still needs to be added.
Detailed instructions for installing Release 1 of the ML-Agents Toolkit can be found on the ml-agents repo.
Note that we've already covered the Unity installation needed for this demo and
the UR3 project has the com.unity.ml-agents Unity package as a dependecy. As
such, you can skip the
Install Unity
and
Install the com.unity.ml-agents Unity package
sections. Furthermore, you can explore the UR3 demo scene and run the
pre-trained model without any additional installation. You only need to install
the ML-Agents Python packages if you're interested in training the robotic arm.
After you have complete the installation, open the ArmRobot folder in Unity.
Then open Scenes > ArticulationRobot.
All manual control is handled through the scripts on the ManualInput object. The scene
is set-up for manual control - hit the Play button in the Unity Editor and experiment
with moving the arm using the controls defined below:
A/D - rotate base joint
S/W - rotate shoulder joint
Q/E - rotate elbow joint
O/P - rotate wrist1
K/L - rotate wrist2
N/M - rotate wrist3
V/B - rotate hand
X - close pincher
Z - open pincher
space - instant reset
Note that ManualInput must be set inactive in the scene if you are using the Agent to control the arm and vice-versa.
In this project, we used the Unity ML-Agents Toolkit to train the robot to touch the cube.
The agent controls the robot at the level of its six joints in a discrete manner. It uses a 'joint index' to select the joint, and an 'action index' to move that joint clockwise, counterclockwise, or not at all. For observations, the agent is given the current rotation of all six joints and the position of the cube.
The reward at each step is simply the negative distance between the end effector and the cube. The advantage of this is that changes in reward are continuous and it does incentivize the agent to pursue our goal of touching the cube. However, other reward schemes may work as well or better. You should experiment!
The episodes end immediately when the robot touches the cube, and are limited to a maximum of 500 steps. At the beginning of each new episode, the robot is reset to its base pose, and the cube is moved to a random location on the table.
This project comes with a pre-trained model using the ML-Agents Toolkit. To see that behavior
in action, just uncheck the ManualInput object in the Hierarchy window and check the MLAgents
object. Then hit Play in the Unity Editor.
You can also train the arm yourself. Detailed instructions on how to train using the ML-Agents Toolkit can be found on the ml-agents repo.
To start training, just run this command:
mlagents-learn ur3_config.yaml --run-id=[YOUR RUN ID]
Then, press Play in the Unity Editor.
As the training runs, a models and a summaries folder will be automatically created in the root level of this project. As you might guess, the models folder stores the trained model files, and the summaries folder stores the event files where Tensorflow writes logs.
To monitor training, navigate into the summaries folder and run:
tensorboard --logdir=[YOUR RUN ID]_TouchCube
You can then view the live Tensorboard at localhost:6006.
Since there is some randomness in the training process, your results might not look exactly like ours. Our reward gradually increased during training, as expected:
Since the reward was quite noisy, we used heavy smoothing in this graph to more easily see the trend. Tensorboard makes this easy, and you might want to try the same.
This demo is provided as-is without guarantees. Please submit an issue if:
- You run into issues downloading or installing this demo after following the instructions above.
- You extend this demo in an interesting way. We may not be able to provide support, but would love to hear about it.